11. Perceptron Algorithm
Perceptron Algorithm
And now, with the perceptron trick in our hands, we can fully develop the perceptron algorithm! The following video will show you the pseudocode, and in the quiz below, you'll have the chance to code it in Python.
Perceptron Algorithm Pseudocode
INSTRUCTOR NOTE:
There's a small error in the above video in that W_i should be updated to W_i = W_i + \alpha x_i (plus or minus depending on the situation).
Coding the Perceptron Algorithm
Time to code! In this quiz, you'll have the chance to implement the perceptron algorithm to separate the following data (given in the file data.csv).
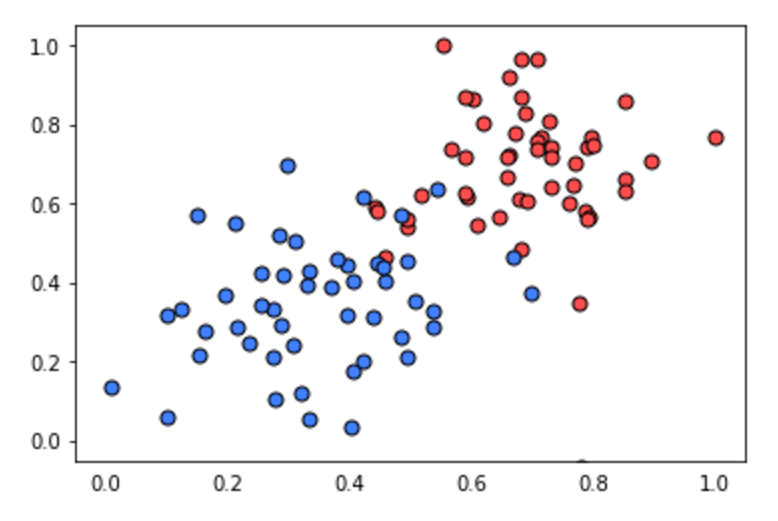
Recall that the perceptron step works as follows. For a point with coordinates
(p,q), label y, and prediction given by the equation \hat{y} = step(w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + b):
- If the point is correctly classified, do nothing.
- If the point is classified positive, but it has a negative label, subtract
\alpha p, \alpha q, and
\alpha
from
w_1, w_2,
and
b
respectively. - If the point is classified negative, but it has a positive label, add
\alpha p, \alpha q,
and
\alpha
to
w_1, w_2,
and
b
respectively.
Then click on test run to graph the solution that the perceptron algorithm gives you. It'll actually draw a set of dotted lines, that show how the algorithm approaches to the best solution, given by the black solid line.
Feel free to play with the parameters of the algorithm (number of epochs, learning rate, and even the randomizing of the initial parameters) to see how your initial conditions can affect the solution!
Start Quiz: